Mapping methodologies used to map landslides along King County river corridors King County
landslide, the movement downslope of a mass of rock, debris, earth, or soil (soil being a mixture of earth and debris).
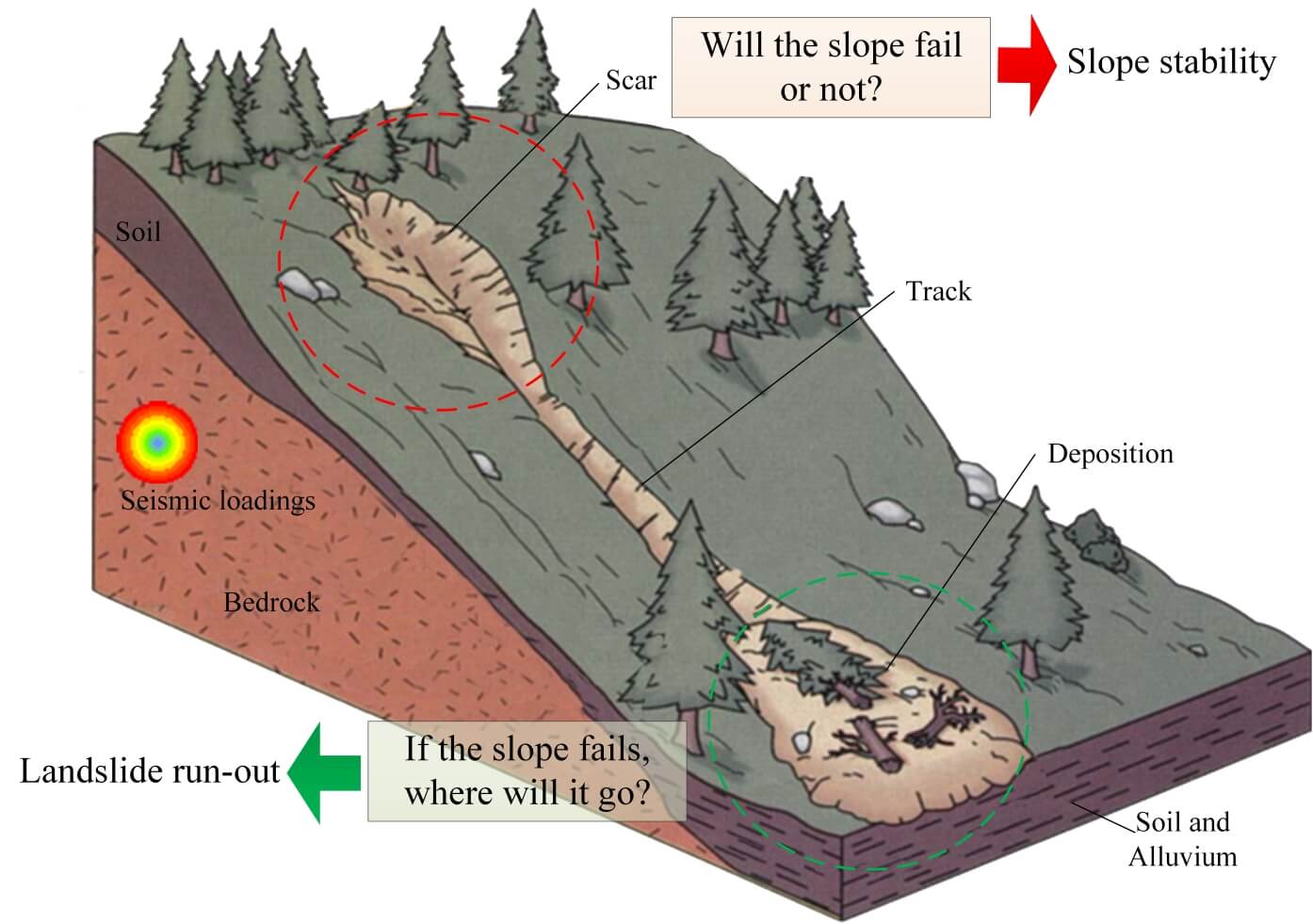
Stability and Runout Analysis of Earthquakeinduced Landslides IntechOpen
Learn what a landslide is by exploring different types of landslides, what causes a landslide, the impact of landslides, and seeing a diagram of a landslide. Updated: 11/21/2023 Table of.

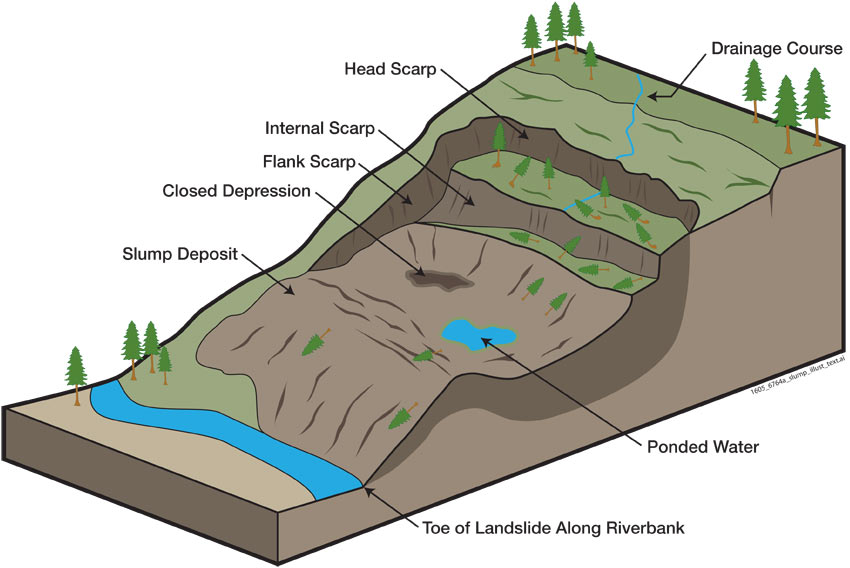
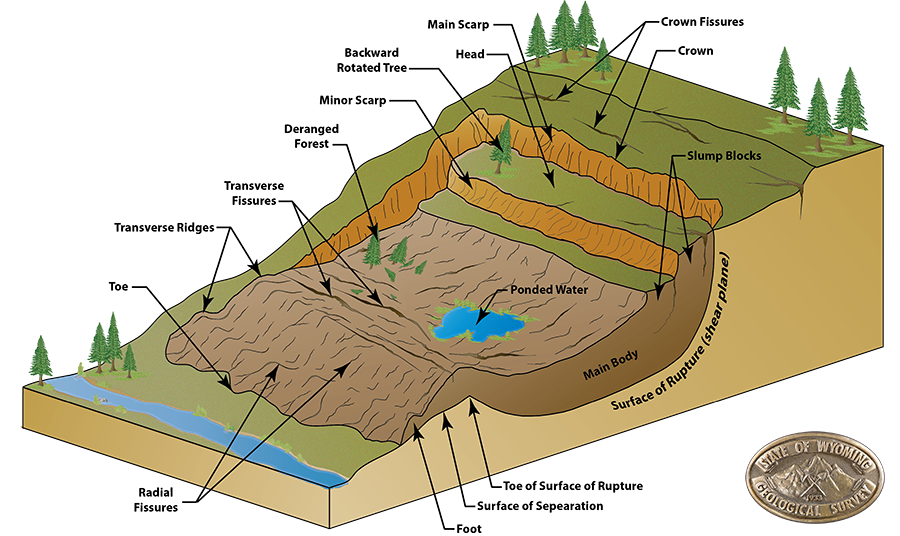
Block diagram of a typical landslide and its component (USGS, 2009) Download Scientific Diagram
ENCYCLOPEDIC ENTRY Landslide A landslide is the movement of rock, earth, or debris down a sloped section of land. Grades 6 - 12+ Subjects Earth Science, Geology, Geography, Human Geography, Physical Geography Photograph Proof of a Landslide
Earth’s Forces ETEAMS
This handbook helps homeowners, community and emergency managers, and decisionmakers to take the positive step of encouraging awareness of available options and recourse in regard to landslide hazard. We provide a list of references, available in print or on the World Wide Web (Internet), that can be used for further knowledge about landslides.

Idaho Geological Survey Landslides
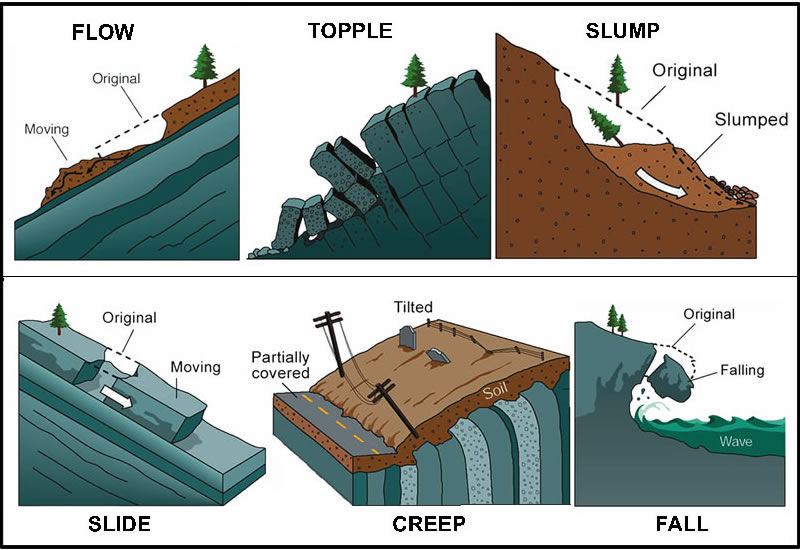
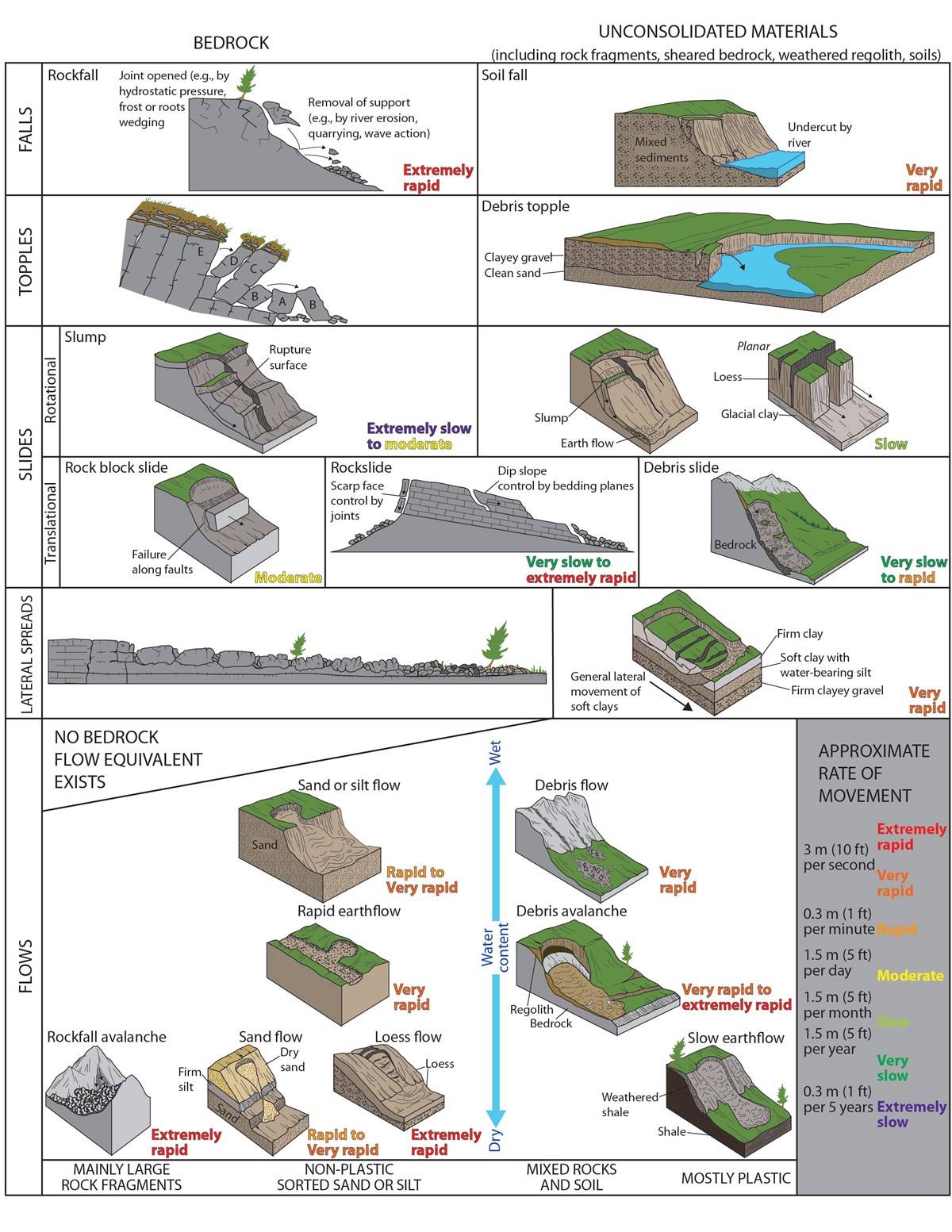
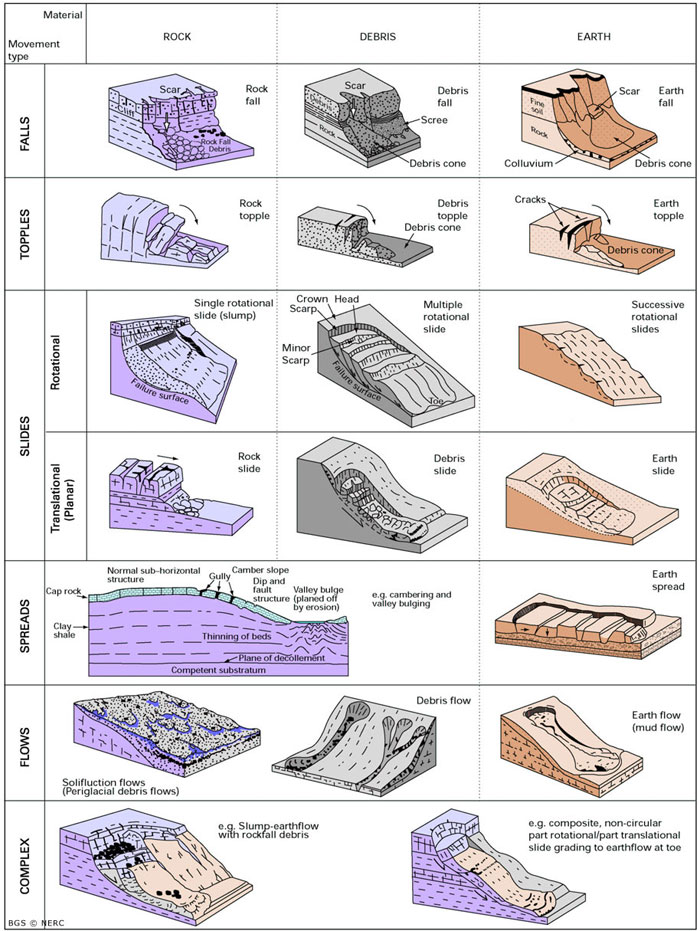
The term "landslide" describes a wide variety of processes that result in the downward and outward movement of slope-forming materials including rock, soil, artificial fill, or a combination of these. The materials may move by falling, toppling, sliding, spreading, or flowing.

Active landslide geomorphic evolution and deepseated landslide... Download Scientific Diagram
The term "landslide" describes a wide variety of processes that result in the downward and outward movement of slope-forming materials including rock, soil, artificial fill, or a combination of these. The materials may move by falling, toppling, sliding, spreading, or flowing.

5 Examples of landslide mechanisms and mass wasting processes... Download Scientific Diagram
Figure 10.4.1 10.4. 1: Approximate extent of Markagunt Gravity slide. Markagunt Gravity Slide: About 21-22 million years ago, one of the biggest land-based landslides yet discovered in the geologic record displaced more than 1,700 cu km (408 cu mi) of material in one relatively fast event. Evidence for this slide includes breccia.

UGS Landslide Illustrations by Jeremy Gleason at
What is a landslide? A landslide is a mass movement of material, such as rock, earth or debris, down a slope. They can happen suddenly or more slowly over long periods of time. When the force of gravity acting on a slope exceeds the resisting forces of a slope, the slope will fail and a landslide occurs.
Landslide Hazards Geohazards (U.S. National Park Service)
This diagrams also reflects conditions of geology surrounding Vaiont Dam. If people dig into the base of a slope to create a road or a homesite, the slope may become unstable and move downhill. This is particularly dangerous when the underlying rock layers slope towards the area.

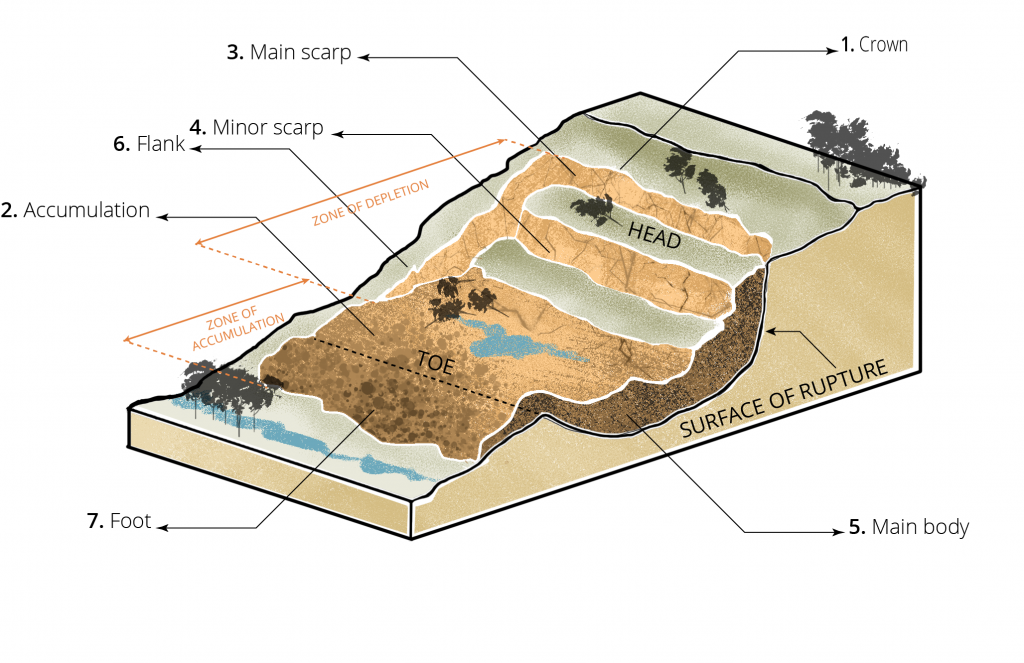
Diagram of deepseated landslide, from USGS Fact Sheet 30043072 U.S. Geological Survey
A landslide is defined as the movement of a mass of rock, debris, or earth down a slope. Landslides are a type of "mass wasting," which denotes any down-slope movement of soil and rock under the direct influence of gravity. The term "landslide" encompasses five modes of slope movement: falls, topples, slides, spreads, and flows.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/rockfall-5b7ae564c9e77c002502137a.jpg)
Different Forms and Sizes of Landslides Gallery
Lesson 8: Landslides Hazards. Earthquakes are a major cause of landslides. Landslides occur when masses of rock, earth material, or debris flows move down a slope due to gravity. Landslides can.
Landslide Information help file
The calculation of the safety of a sliding block on a plane (a layered slide with preferential failure along pre-existing weaknesses) is shown below in figure 1. This calculation takes into account slope angle, friction, cohesion, and water content. Increasing water content and slope angle decreases the factor of safety.
Landslide Morphology Landslide Mitigation
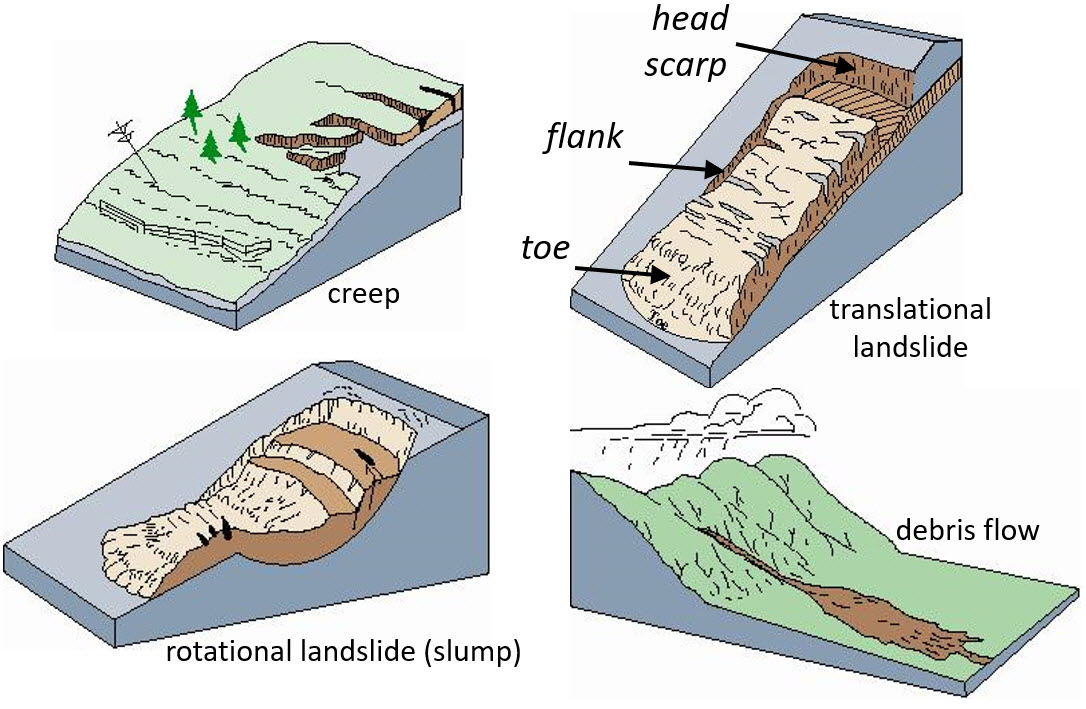
Slides. Figure 3. These schematics illustrate the major types of landslide movement. Although many types of mass movements are included in the general term "landslide," the more restrictive use of the term refers only to mass movements, where there is a distinct zone of weakness that separates the slide material from more stable underlying material.

Mass Movement Geography
The term "landslide" describes a wide variety of processes that result in the downward and outward movement of slope-forming materials including rock, soil, artificial fill, or a com-bination of these. The materials may move by falling, toppling, sliding, spreading, or flowing.
Landslides
Therefore, α1α2α3 = 1 and β1 + β2 + β3 = 1. For graphical data presentation, β1, β2, β3 are the tools for interpreting the landslide geometry. The ternary diagram shown in Fig. 10 clearly demonstrates the differences between the three landslides observed. SL have smaller L , W, and H, and similar average β1 and β2.
The Haverstraw Landslide Feb. 1, 2018 The Catskill Geologist
Includes diagrams of different landslide types. The Landslides Handbook- A Guide to Understanding Landslides (Handbook), U.S. Geological Survey This comprehensive resource for a lay audience includes detailed information on types of landslides, where landslides occur, landslide causes, and landslide effects/consequences.